Sources of Good and Bad Omega Essential Fatty Acids

Essential fatty acids are important nutrients for your brain, heart, immune system, and skin. They play vital roles in regulating inflammation, hormone health, mood and cognition.
You need a good balance of omega-3, 6, and 9 in your diet, because different omega fatty acids are important for the body in different ways.
What Are Essential Fatty Acids?
Your body can synthesize some of the omega fatty acids from the foods you eat. However, there are some omega fatty acids that your body can’t make on its own and must be consumed in the diet. These are called essential fatty acids. There are only 2 omega fatty acids that are essential, and they are omega-3 alpha linolenic acid (ALA) and omega-6 linoleic acid (LA).
Are Omega-6 Fatty Acids Bad for You?
It is often said that omega-3 is anti-inflammatory and omega-6 is pro-inflammatory. So you may think that omega-6 is bad for you and it is all to be avoided.
But this raises an interesting question: how can something that is essential for your body, which you must consume in your diet in sufficient amounts for good health, be bad for you at the same time?
Well, It turns out that there are some sources of omega-6 fatty acids that can cause heart disease, inflammation, hormone imbalance, pain, autoimmunity, and neurodegeneration. But other sources of omega-6 fatty acids are actually essential for your body!
In this article, you will learn what these damaging sources of omega-6 fatty acids are and why you want to avoid them, and why the food manufacturers (and even your doctors) may not tell you about them.
Best Sources of Essential Fatty Acids
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
EPA and DHA Fatty Acids

Animal fats contain omega-3 fatty acids in the form of EPA and DHA. EPA tends to have systemic anti-inflammatory effects, and may confer more benefit for cardiovascular health. DHA tends to have more benefit for brain health, by supporting healthy levels of brain inflammation and contributing to neuronal cell membrane and myelin sheath formation.
Animal Foods high in omega-3 EPA/DHA:
SMASH fish:
- Salmon – 2.1 g/ser
- Mackerel – 4.5 g/serv
- Anchovy – 400 mg /serv
- Sardine – 2.1 g/serv
- Herring – 2.1 g/serv
These fish are usually also good sources of vit D, vit B12, selenium.
In addition, the following seafood also has good amount of omega-3 EPA/DHA:
- Cod liver oil – also source of Vit A and D
- Oysters – also source of zinc
- Caviar – also source of choline
ALA Fatty Acids

Fats derived from plants such as nuts and seeds contain omega-3 essential fatty acid in the form of ALA, which is a type of polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Plant Foods high in essential omega-3 ALA:
- Walnuts – 2.5 g/serv – also source of manganese, copper, fiber, phenols
- Flax seeds – 2.3 g/serv – also source of fiber, magnesium
- Chia seeds – 5 g/serv – also source of magnesium, manganese, selenium, 5 g protein, 5 g fiber
- Hemp seeds – 3 g/serv – also source of
- Soybeans – 1.4 g/serv – also source of protein, fiber, B vitamins, vit K
How to Get Enough Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Your Diet
It’s important to include enough omega-3 sources in your diet, since your body can’t make these fatty acids on its own!
First, make sure that you are eating the foods listed above. Additionally, here are some other food sources with lower amounts of omega-3s:
- pasture-raised eggs
- grass-fed meat and dairy
- vegetables such as spinach, Brussels sprouts, and purslane
Keep in mind that many of these foods also have a good amount of omega-6 fatty acids.
ALA can convert into EPA and DHA in humans, but this conversion is very inefficient and does not yield enough EPA and DHA for optimal health.
Therefore supplementation with EPA and DHA with fish oil in the range of 2-4 grams per day is recommended for optimal omega-3 fatty acid status. Here is the one I recommend.
If you are vegetarian or vegan, consider supplementing with algae omega-3 EPA/DHA instead.
Omega-6 Fatty Acids
LA (Linoleic Acid)

omega-6 linoleic acid (LA) is another polyunsaturated fatty acid that is essential for health and must be consumed from the diet.
Healthy sources of essential omega-6 LA:
- Walnut – 10.8 g/serv
- Hemp seed – 8 g/serv
- Pecans – 5.8 g/serv
- Sunflower seed – 6.5 g/serv
- Pumpkin seed – 5.6 g/serv
- Pistachios – 3.7 g/serv
- Almonds – 3.6 g/serv
When you consume LA, your body can convert it to other omega-6 fatty acids downstream: gamma linolenic acid (GLA) and arachidonic acid (AA).
GLA (Gamma Linolenic Acid) and AA (Arachidonic Acid)

These omega-6s are called non-essential fatty acids, because your body can make them on its own.
You can also consume GLA and AA from the diet.
- Sources of GLA include evening primrose oil, borage oil, and black currant seed oil.
- Sources of AA include animal proteins, organ meat, fish, and eggs.
GLA tends to have an anti-inflammatory effect. AA tends to have a pro-inflammatory effect. But your body will synthesize GLA and AA based on the innate intelligence of the body’s needs.
However, over consumption of AA can push the eicosanoids (fat-based signaling molecules involved in your immune response) into a pro-inflammatory state that can lead to symptoms and disease. This is especially common in the presence of other sources of inflammation from injuries, autoimmune disease, arthritis, and metabolic disease such as diabetes,
As you can see from this list, there are a lot of foods that have both omega-3 and omega-6. If you are eating whole fresh food that is all natural, it’s going to have a lot of different “nutrients.” And that’s goodness for us because God or nature already balanced all the different nutrients for us in natural food.
However, if you eat man-made processed foods, it’s going to have a lot of “ingredients.” Red #40, potassium sorbate, and hydrogenated fats can all be in the ingredient list of processed foods. But you are kidding yourself if you call these artificial ingredients nutrients. And that’s what food manufacturers want you to believe: that just because something is edible, then it’s been tested and researched to be safe, so don’t ask any questions.
Therein lies the problem. There is very strong evidence showing that high intake of omega-6 to omega-3 ratio found in the typical Standard American Diet is harmful for health. But there is some conflicting information about exactly how much omega-3 and omega-6 you need. And some experts say that there is no reason to avoid omega-6 fats because they are necessary and not to be avoided.
While it’s true that omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids are both essential to our health, it’s the quality of the fats and how they are processed that makes a huge difference in their effects. This is where the industrial seed oil, which is ubiquitous in the Standard American Diet, is a major contributor to the chronic inflammatory and degenerative conditions facing many Americans today.
Industrial Seed Oils
Industrial seed oils, often called vegetable oils, and often includes the term oil shortening, typically uses plants with high omega-6 content. High consumption of omega-6 fatty acids (while not getting enough omega-3 fatty acids) skew the ratio of balance of these nutrients. That alone can promote more inflammation in your body and lead to symptoms and diseases.
Industrial seed oils include:
- Sunflower oil – 9 g/serv
- Soybean oil – 7 g/serv
- Cotton seed oil (Crisco) – 7 g/serv
- Safflower oil – 3.4 g/serv
- Canola oil – 2.6 g/serv
- Corn oil – 2.4 g/serv

These highly processed oils can have deleterious effects on your health. The reason lies in how they are made. In fact, here are 6 reasons why you will think twice about consuming them:
- Unlike olives and coconut which are easy to press, the seeds are naturally low in oil. Therefore they are treated with hexane to extract more oil from them. Hexane is a petroleum-based solvents that have the potential to cause nervous system toxicity, liver and kidney damage, respiratory issues, and other health problems.
- These seed oils are also treated with high heat as a method to sterilize. These PUFA’s are unstable in high temperature and readily oxidize with high temperature, which creates free radicals that damage your cells and DNA, increasing inflammation and risk for cancer.
- Even worse, these seed oils can go through the process of shortening, which is the process of adding hydrogen, or hydrogenating the fat to turn the vegetable oil into a white solid that has a buttery consistency. This hydrogenated oil is often used as a substitute for butter in baking.
For a long time, food manufacturers were pitting saturated fat as the culprit of heart disease, and claiming that hydrogenated fat, and its evil cousin partially-hydrogenated fat, aka trans fat, are healthier alternatives. They even got the FDA to allow them to label these products as “heart healthy” in the 80’s and 90’s.
They were considered healthy until they weren’t. Strong and ample evidence has shown that hydrogenated fats and trans fats actually cause heart disease by lowering good HDL cholesterol, and raising bad LDL cholesterol. These processed and synthetic fats cause heart disease, stroke, diabetes, and many diseases of inflammation. So much so, that in fact the FDA who initially endorsed these fake fat has now deemed trans fat as not generally regarded as safe (GRAS), and have banned the use since June 18, 2018.
- And if that is not enough to steer you away, the seed oils have an undesirable smell with the solvents and damage from high heat. So they are again chemically treated to deodorize the oils. This process can produce trans fat, with its known toxic and disease-causing effects. But trace amounts less than 0.5 gram are still allowed and not required to be disclosed on labels, despite Harvard researchers have warned since the 1990s that there are no safe limits to trans fat intake.
- To add insult to injury, during the industrial processing of seed oils, contaminants like pesticides and heavy metals can be introduced. The seeds and plants that are used are usually genetically modified organisms, which are resistant to glyphosate and has led to increased use of these herbicides that may impact the gut microbiome, disrupt endocrine function, and potentially be carcinogenic.
- Finally, industrial seed oils are commonly found in processed and fast foods, which are often fried. This creates oxidation and rancidity, and is high in refined sugars, refined grains, and unhealthy additives. These processed seed oils and their accomplices reinforce poor eating habits that make you crave these unhealthy synthetic foods. Regular consumption of these foods can lead to weight gain, poor nutrition, and increased risk for various health issues.
The combination of these factors listed above strips all the other nutrients that are naturally occurring in the plant, and turns these industrial processed seed oils into something that functions very differently from the healthy natural omega-6s that you get in real food.
In fact, these industrial processed vegetable oils and seed oils have been linked to cardiovascular disease, cancer, metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, obesity, Alzheimer’s disease, cognitive decline, depression, non-alcoholic fatty liver, asthma, and hormone imbalance.
It’s important that you understand the difference between natural omega-6 from real food and synthetic omega-6s from industrial seed oils and other synthetic man-made fats. When your intake of omega-6s is properly balanced with natural omega-3s, it is health promoting.
So consuming actual sunflower seeds and soybeans in their natural and organic form is not a problem, versus consuming the processed oils from those same foods.

Research suggests that ideal omega-6 to omega-3 ratios for optimal health to be between 1:1 to 4:1. So for every 1 to 4 parts of omega-6 intake should be paired with 1 omega-3.
Modern Western diets often have an omega-6 to omega-3 ratio ranging from 10:1 to 20:1 or even higher. This disproportionate ratio is primarily due to the high consumption of industrial seed oils (rich in omega-6) and a relatively low intake of foods rich in omega-3 (such as fatty fish, flaxseeds, and walnuts).
Here is the good news. Now that you know the sobering facts about the bad processed fats, there is hope and you can make simple changes to turn your health around with the right fats. In fact, switching out the bad fats with healthy natural fats can make a significant and noticeable difference in your health and quality of life, and can happen relatively quickly, in a matter of weeks to months.
So What Is the Best Way to Improve Your Essential Fatty Acid Levels?
The easiest way to go about improving your omega-6 to omega-3 ratio, is simply minding the quality of the food you are eating. I recommend that you get super picky about the quality of the oil and fats you consume.
You can bring your omega-6 fatty acid intake down to healthy ranges by:
- Severely reducing or completely eliminating the industrial processed seed oils and hydrogenated fats that are often found in processed, packaged, and fast foods. These are commonly found in deep fried foods, potato chips, biscuits, cakes, muffins, store bought salad dressings that contain these seed oils, margarine, dipping sauces, etc.
- Reading the labels of foods you buy. You will be surprised how commonly these industrial seed oils are present! Get picky about the quality of oils and fats you consume, and put them back on the shelf and don’t eat them when you spot them.
- Substituting vegetable oils with extra virgin cold pressed olive oil, coconut oil, avocado oil, or macadamia nut oil.
Next, increase natural healthy omega-3 fatty acid intake by:
- Incorporating more real food such as fatty fish and raw nuts and seeds.
- Supplementing with high-quality fish oil. Remember that plant based omega-3 essential fatty acid alpha linolenic acid can convert to omega-3 fatty acid EPA and DHA. But that process is very slow and not sufficient for optimal health, so I always recommend supplementing.
- My favorite is Omega Pure Pro in the 2-4 gram per day range.
- If you prefer vegetarian sources, you can find algae based omega-3 supplements that will provide EPA and DHA to support brain health and heart health. (To get the best price on my recommended algae-based supplement, create a free Fullscript account here and search for Algae Omega by Nordic Naturals.)
What About Omega-9 Fatty Acids?

Omega-9 fatty acids such as oleic acid are monounsaturated fatty acids. Omega-9 fatty acids are called non-essential fatty acids. This does not mean they are not important to your health. It just means that your body can synthesize them from other fats that you eat, so you don’t have to get them from your diet.
Omega-9 fatty acids have been shown to lower LDL bad cholesterol and therefore decrease your risk of heart disease and stroke. Omega-9s may also support healthy insulin and blood sugar control, benefit blood vessel health, reduce risk for neurodegeneration such as Alzheimers, and have anti-inflammatory properties in the skin, lung, eye, liver, and intestines.
Sources of omega-9 monounsaturated fatty acids:
- Olive oil 7.1 g/100g serv
- Avocado oil 6.7 g/100g serv
- Sesame seeds 6.7 g/100g serv
- Pumpkin seeds 5.7 g/100g serv
- Macadamia nut oil 5.5 g/100 g serv
- Cashew nuts 2.5 g/100g serv
- Goose fat 3.6 g/100g serv
- Peanut butter 3.4 g/100g serv
- Rape seed oil 9.2 g/100g serv
- Corn oil 4.8 g/100g serv
- Sesame oil 3.9 g/100g serv
Just as with all the other omega fatty acids, you will see different ratios of omega-3, 6, and 9 in almost all natural healthy fats. You don’t have to worry about supplementing with omega-9 fatty acids, since normal fat consumption will allow your body to synthesize omega-9 on its own.
So How Much Omega-3, 6, and 9 Should You Include in Your Diet?
That depends on your current caloric intake, health status and goal. There may be times and situations where you would want to measure your daily macronutrient intake in trying to hit a specific amount of caloric intake and a specific amount of fat.
For example, a ketogenic diet versus a Mediterranean Diet will have significantly different amounts of fat intake and therefore omega fatty acid intake.
If you are on a 1,500 calorie/day diet, this will have different amounts of fat compared to if you are on a 2,500 calorie/day diet.
There are a lot of variables and therefore it is not practical to think in terms of absolutes regarding the exact amount of fat intake you should have, unless you are working with me or a healthcare professional experienced in this.
For general health, it is more important that you eat a balance of fats, proteins, and carbs. And within the fats, a balance of saturated, MUFA, and PUFA. And within the PUFAs, a balance of omega-3, 6, and 9.
Rule of Thirds
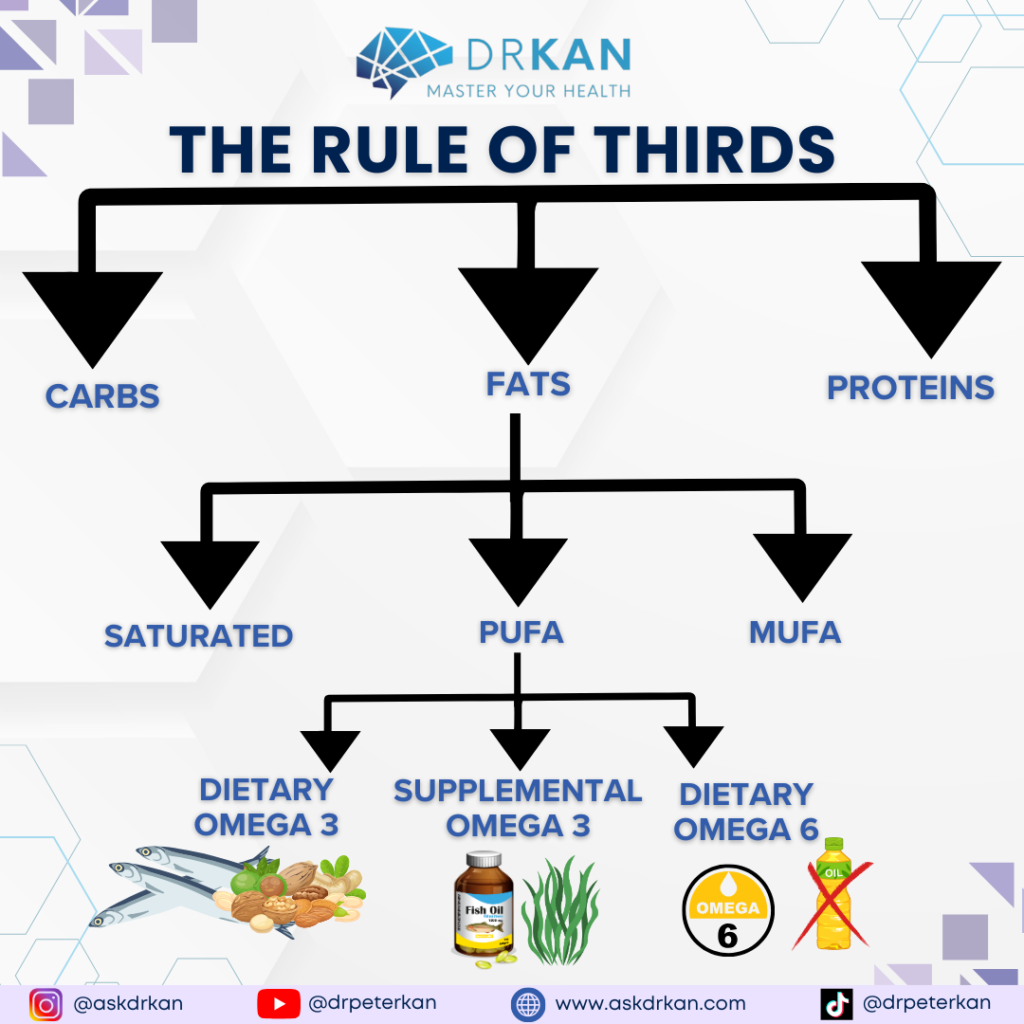
An easy rule of thumb that I use with my clients that makes this super simple and effective is the Rule of Thirds.
⅓ of total daily intake from fats, ⅓ from protein, ⅓ from carbs.
And within that ⅓ of fat intake, divide that into ⅓ saturated fats, ⅓ MUFA, ⅓ PUFA.
And within the PUFA, reduce industrial seed oil to reduce harmful man made omega-6 without unnecessarily cutting out natural omega-6 from whole foods, while increasing intake of fatty fish and nuts and seeds to increase omega-3s.
Supplement with omega-3 EPA/DHA since conversion from plant source omega-3 ALA to EPA/DHA is slow and inefficient in the human body. Consider taking a high quality and high potency fish oil supplements such as the Omega Pure Pro in the 2-4 gram per day range, and if you are vegetarian take algae omega-3 supplements.
Here Are Some Pro Tips When It Comes to Supplements:
It is best to take omega fatty acid supplements with meals to take advantage of the increased digestive secretion that is already occurring with the meal to maximize absorption.
If you get the fish oil repeat where you burp up the fish oil taste with fish oil gelcaps, try putting the bottle in the freezer. This way it will take longer for the frozen gel cap to dissolve, allowing it to settle lower in your intestinal tract and reduce the chance of you burping up the fish oil.
If you have difficulty digesting fatty foods due to gallbladder dysfunction or if gallbladder has been removed, consider taking bile support such as Cholecys Pro that contains cholagogues that support thinning and releasing of b
ile from liver and gallbladder.
Conclusion
Now you know the sources of different essential fatty acids, and how to get picky about the quality of fats you’re consuming. You know how to reduce or eliminate industrial seed oils or vegetable oils, and you can use the rule of thirds to get a good balance of all the nutrients and essential fats.
By learning to read labels and being intentional about making healthy choices, you can improve your omega fatty acid balance and improve your health in more ways than you know.
Want Some Help?
We offer Zoom consultations to help you identify the root cause of your health struggles. We order functional medicine lab tests for you and design a customized eating plan, supplementation plan and detoxification plan to optimize health while reducing the dependency on medications.
If you’re struggling with chronic symptoms, and looking for root cause approach using a natural and holistic approach, please click the link below for more information and to get started on the path to wellness.
